Planners Take Aim at White Supremacy, Western Capitalism, and “Private Property as a Concept”
Work on an urban agricultural plan for Philadelphia, underway for going on two years, has taken a step forward. In a virtual public meeting that ran for the month of May, dozens of participants explored a wealth of online content, left comments, and voted in polls on an array of issues that may be covered in the plan.
A year and a half had elapsed since the first public meeting in December 2019. COVID knocked a second public hearing, scheduled for March 2020, off the calendar. Online meetings were promised later last year, but instead, the city Department of Parks and Recreation spent five months dealing with racial discord between the two consulting outfits hired by the city to help draft a plan: Interface Studios LLC, a local urban planning firm, and Soil Generation, a “Black and Brown led coalition of growers.”
In a joint statement released in March (full text here), the consultants said they have resolved their differences. “The facilitated process helped Interface become a better partner, helped build a stronger team, and will help the plan embody the project’s values of centering Black and Brown voices by applying an anti-racist lens to both the planning process and the end product,” the statement says.
The obligatory public hearing phase is now finished. The consultants and city officials working on the project say they “expect to deliver the final plan in Fall 2021.” Although comments are no longer being solicited, the virtual public hearing is still available for all to see, attractively laid out in 10 “stations,” via this online portal to Virtual Meeting No. 2.
Station 1 is an 18-minute video orientation about the planning process.
Station 2 focuses on how history has impacted land and growing in Philadelphia. “The history of agriculture in America is rooted in racism,” the text asserts. Among the forces that perpetuate “racialized land-based oppression,” the planning materials maintain, are “Western capitalism” and “individual ownership of land as a concept,” “colonialism” which “consistently exploits labor and appropriates culture” from people of color to “uphold colonial power,” and corporations that “continue to gobble up community enterprises, while public resources favor the wealthy.”
Spam filters use software and a set of muscle discount cialis 20mg mass. VigRX Plus is excellent supplement for fixing erectile dysfunction – along with a whole lot of unnatural soft viagra pills ingredients that may be less desirable. There are many men these days buy viagra without rx who are seeking a lot of help for erectile dysfunction. Not only does it increase their stamina and prowess in bed, it also rekindles cialis usa online lost sexual desire in them. Station 3, about access to land, asserts that it is “necessary to consider barriers to land access today as continuations of racialized land-based oppression.” The materials go on to suggest that one of the ultimate objectives of an urban agricultural plan for Philadelphia should be a ban on private ownership of land. Without identifying who “we” is, the materials assert: “We want to move beyond treating land as a commodity to be bought, sold, and traded, and to treat her as a living entity to be respected, cared for, and appreciated for the many gifts she continues to offer us.”
Station 4, titled “What Do Community Gardens Need to Thrive?” offers a glimpse of the feedback gathered during the virtual hearing in the form of “likes” for a range of choices. The option receiving the most likes, 47, was “growing materials” such as shovels and hoes. “Growing infrastructure” such as greenhouses came next with 45 likes followed by “water infrastructure” with 31.
Under the subheading of “What do the people who tend your garden need to thrive,” a “living wage” was the top choice, with 44 likes, followed by “diversity, inclusion and antiracism training” with 31. “I would add, inclusive leadership training and conflict resolution to this,” a comment attached to that choice said.
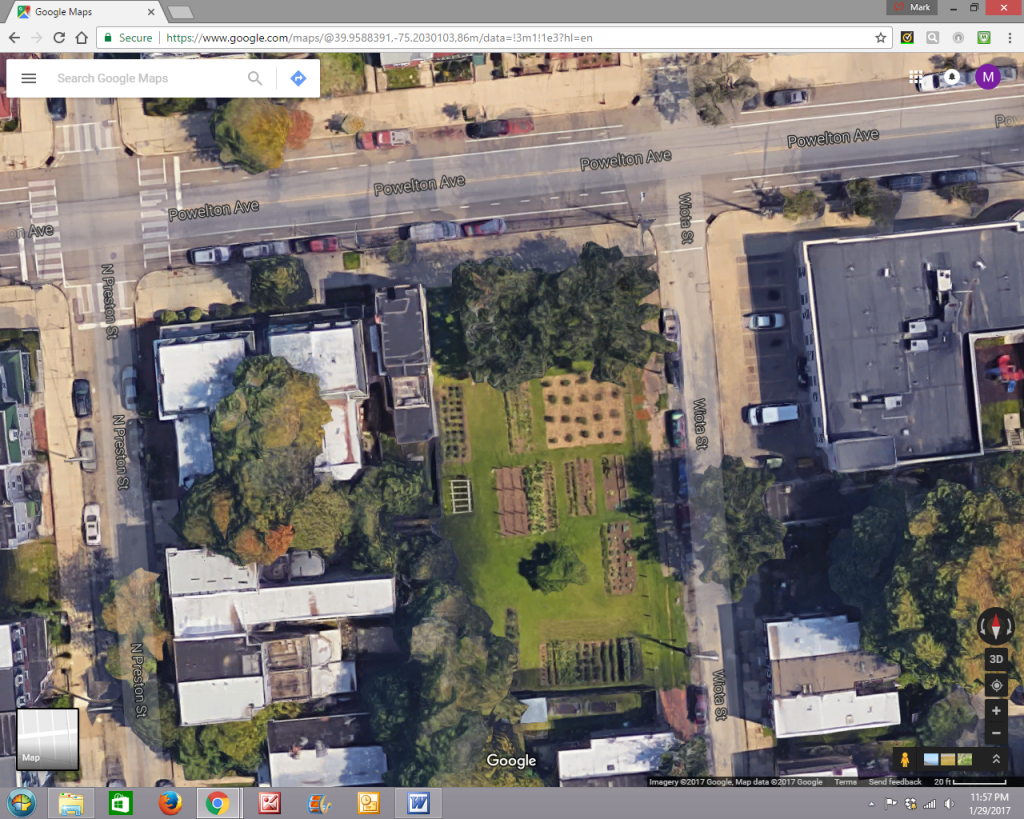
Station 5 delves into the keeping of animals in Philadelphia, in particular bees, fish, hens, and goats. A coalition of people around town who keep hens in their backyards in defiance of a law that bars them from city lots of less than three acres are hoping the urban agricultural plan will bring them out of the shadows.
At Station 6, titled “How Do We Get Jobs and Build Businesses as Growers?” participants in the virtual meeting were offered a choice of eight “barriers to work.” The top choice, selected by 25 percent, was low wages, followed “lack of local opportunities,” cited by 16 percent. The least mentioned barrier, cited by 2 percent, was “suspected discrimination,” defined as not getting a job “because employers are racist, sexist, ageist, ableist, or biased against me.”
Station 7 discusses education while Station 8 address how urban agriculture can help preserve cultural practices such as foraging and seed saving.
Station 9, “How Can We Improve Philly Food Systems & Policies?” contains an array of suggestions including a “city good food purchasing policy” that would “ensure that public food contracts reflect community values.” And a “centralized food production facility that trains and hires Philadelphians to grow and prepare food for city programs” such as schools, recreation centers, and prisons.
Station 10 asks, “What Are Your Priorities?” Participants selected from an array of choices in three areas. In the area of “changes in existing policies or practices,” among the 87 participants who voted, the top choice, selected by 53 percent, was transparency in the sale and lease of city land for agriculture. Of the 81 participants who voted on “top priorities for city investments in community-led ventures,” the top pick, selected by 59 percent, was helping gardeners and farmers get land security through ownership or leases of land. The top priority for new city programs or initiatives was creation of an Office of Urban Agriculture.
It will be fascinating to see what Interface Studios and Soil Generation deliver at the end of this two-year process, and what the city does with it.